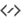Silnik pędzla spreju¶
Pędzel, który może rozproszyć cząsteczki naokoło w obszarze swojego pędzla.
Ustawienia¶
Koniuszki pędzli (Używany jako cząsteczka, gdy kształt spreju nie jest włączony)
Obszar spreju¶
Here you can set different properties related to the area where the particles are distributed and how they are distributed.
Area¶
- Średnica
Rozmiar obszaru
- Współczynnik kształtu
Jest to współczynnik kształtu: 1,0 oznacza w pełni okrągły.
- Kąt
Kąt rozmiaru spreju: działa dobrze ze współczynnikami kształtu innymi niż 1,0.
- Skala
Zwiększa średnicę.
- Odstęp
Zwiększa odstępy średnicy spreju.
- Fluktuacyjny ruch
Zakłóca obszar sprejowania dla uzyskania dodatkowej losowości.
Cząsteczki¶
- Amount
- Liczba
Use a specified number of particles.
- Gęstość
Use a percentage for the number of particles.
- Distribution
Added in version 5.1.
Here you can set how the particles are distributed in the spray area. The particles are distributed using polar coordinates, so you can set different distributions for the angle and the distance of the particles relative to the center of the spray area.
- Angular
You can specify how the particles are distributed around the center using one of the following options:
Uniform: Distributes the particles uniformly. Each angle is equally likely to receive a particle.
Curve: You can set a custom curve that models how the particles should be distributed. The left side of the curve represents an angle of 0 degrees and the right side an angle of 360 degrees. Higher values in the vertical direction mean that there is a higher probability that a particle ends up at that particular angle. In the spray area the angle increases clockwise.
Repeat: Have the curve repeat itself multiple times from 0 to 360 degrees. Without this, you would need to build a very complex curve with too many control points to achieve the same result.
- Radial
You can specify how the particles are distributed from the center to the edge of the spray area using one of the following options:
Uniform: Distributes the particles uniformly.
Center-biased spread (legacy): This option ensures compatibility with the brushes made prior to version 5.1. Before, the particles were distributed uniformly in terms of distance from the center, but that ended up concentrating more particles in the center of the spray area from a 2d space perspective. For example, a circumference at a distance of 10 pixels from the center ended having roughly the same number of particles as a circumference at a distance of 100 pixels, while being 10 times smaller in length.
Gaussian: distributes the particles using a gaussian or normal distribution.
Standard deviation: Sets the standard deviation of the distribution. Higher values will make the particles more spread.
Center-biased spread (legacy): This option ensures compatibility with the brushes made prior to version 5.1. See the previous point for more information.
Cluster: This will allow you to quickly concentrate the particles towards the center or the edge of the spray area.
Clustering amount: Positive values will make the particles concentrate towards the center of the spray area. Negative values will make the particles concentrate towards the border of the spray area. Values near 0 will make the particles spread more uniformly.
Curve: You can set a custom curve that models how the particles should be distributed. The left side of the curve represents the center of the spray area and the right side represents its border. Higher values in the vertical direction mean that there is a higher probability that a particle ends up at that particular distance.
Repeat: Have the curve repeat itself multiple times from the center of the spray area to its edge. Without this, you would need to build a very complex curve with too many control points to achieve the same result.
Different distribution types on display:¶
Uniform for both Angular and Radial, with Center-biased spread (legacy) turned on.
Uniform for both Angular and Radial, with Center-biased spread (legacy) turned off.
Clustered for Radial, with Clusting Amount: 0.0.
Clustered for Radial, with Clusting Amount: -5.0.
Clustered for Radial, with Clusting Amount: +5.0.
Curve for Angular, using the default curve and 0 repeats.
Curve for Angular, using the default curve and 5 repeats.
Curve for Radial, using the default curve with 3 repeats.
Curve for Angular using a hill shaped curve, 7 repeats, and Clustered for Radial, with Clusting Amount: -5.0.
Gaussian for Radial, with Standard Deviation: 25.
Gaussian for Radial, with Standard Deviation: 50.
Gaussian for Radial, with Standard Deviation: 80.
Kształt spreju¶
Po włączeniu, stworzy to daną cząsteczkę. Jeśli nie, to koniuszek pędzla będzie cząsteczką.
- Kształt
Może być…
Elipsa
Prostokąt
Wygładzone piksele
Piksel
Obraz
- Szerokość i wysokość
Określa szerokość i wysokość cząsteczki.
- Proporcjonalny
Blokuje szerokość i wysokość tak, aby były te same.
- Tekstura
Umożliwia wybranie obrazu dla Kształtu obrazu.
Dynamika kształtu¶
- Losowy rozmiar
Czyni rozmiar cząsteczek losowym pomiędzy 1x1 piksel i danym rozmiarem cząsteczki w koniuszku pędzla lub kształcie spreju.
- Stały obrót
Daje stały obrót cząsteczce, z którego później można pracować.
- Losowy obrót
Czyni losowym obrót.
- Waga podążania za wskaźnikiem
Jak bardzo nacisk wpływa na obrót cząsteczek. Przy 1,0 i wysokim nacisku wygląda to tak, jakby cząsteczki eksplodowały ze środka.
- Waga kąta
Jak bardzo kąt obszaru sprejowania wpływa na kąt cząsteczki.
Ustawienia barw¶
- Losowy HSV
Uczyń losowym HSV przy użyciu siły suwaków. Im wyższe, tym więcej barwa będzie odchylona od barwy pierwszoplanowej, z kierunkiem wskazującym kierunek zgodny lub przeciwny do ruchu wskazówek zegara.
- Losowa nieprzezroczystość
Czyni losowym nieprzezroczystość.
- Barwa na cząsteczkę
Czy ustawienia barwy powinny być na cząsteczkę zamiast na obszar.
- Próbkuj warstwę wejściową.
Użyje warstwy leżącej poniżej jako odniesienia dla barw zamiast barwy pierwszoplanowej.
- Wypełnij tło
Wypełnia obszar barwą drugoplanową przed narysowaniem cząsteczek.
- Wymieszaj z barwą drugoplanową.
Nadaje cząsteczce losową barwę spośród barwy pierwszoplanowej/na wejściu/losowej HSV oraz drugoplanowej.