Arithmetic¶
These blending modes are based on simple maths.
Addition¶
Adds the numerical values of two colors together:
Yellow(1, 1, 0) + Blue(0, 0, 1) = White(1, 1, 1)
Darker Gray(0.4, 0.4, 0.4) + Lighter Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Even Lighter Gray (0.9, 0.9, 0.9)
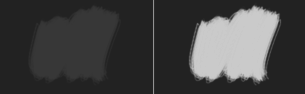
Left: Normal. Right: Addition.¶
Light Blue(0.1608, 0.6274, 0.8274) + Orange(1, 0.5961, 0.0706) = (1.1608, 1.2235, 0.8980) → Very Light Yellow(1, 1, 0.8980)
Left: Normal. Right: Addition.¶
Red(1, 0, 0) + Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Pink(1, 0.5, 0.5)

Left: Normal. Right: Addition.¶
When the result of the addition is more than 1, white is the color displayed. Therefore, white plus any other color results in white. On the other hand, black plus any other color results in the added color.

Left: Normal. Right: Addition.¶
Divide¶
Divides the numerical value from the lower color by the upper color.
Red(1, 0, 0) / Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = (2, 0, 0) → Red(1, 0, 0)
Darker Gray(0.4, 0.4, 0.4) / Lighter Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Even Lighter Gray (0.8, 0.8, 0.8)
Left: Normal. Right: Divide.¶
Light Blue(0.1608, 0.6274, 0.8274) / Orange(1, 0.5961, 0.0706) = (0.1608, 1.0525, 11.7195) → Aqua(0.1608, 1, 1)
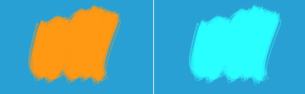
Left: Normal. Right: Divide.¶

Left: Normal. Right: Divide.¶
Inverse Subtract¶
This inverts the lower layer before subtracting it from the upper layer.
Lighter Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)_(1_Darker Gray(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)) = (-0.1, -0.1, -0.1) → Black(0, 0, 0)
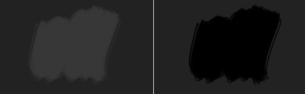
Left: Normal. Right: Inverse Subtract.¶
Orange(1, 0.5961, 0.0706)_(1_Light Blue(0.1608, 0.6274, 0.8274)) = (0.1608, 0.2235, -0.102) → Dark Green(0.1608, 0.2235, 0)
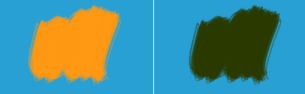
Left: Normal. Right: Inverse Subtract.¶
Left: Normal. Right: Inverse Subtract.¶
Multiply¶
Multiplies the two colors with each other, but does not go beyond the upper limit.
This is often used to color in a black and white lineart. One puts the black and white lineart on top, sets the layer to ‘Multiply’, and then draws in color on a layer beneath. Multiply will allow all the color to go through.
White(1,1,1) x White(1, 1, 1) = White(1, 1, 1)
White(1, 1, 1) x Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
Darker Gray(0.4, 0.4, 0.4) x Lighter Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Even Darker Gray (0.2, 0.2, 0.2)
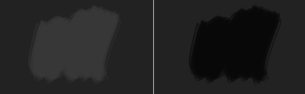
Left: Normal. Right: Multiply.¶
Light Blue(0.1608, 0.6274, 0.8274) x Orange(1, 0.5961, 0.0706) = Green(0.1608, 0.3740, 0.0584)
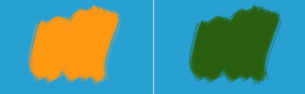
Left: Normal. Right: Multiply.¶
Left: Normal. Right: Multiply.¶
Subtract¶
Subtracts the top layer from the bottom layer.
White(1, 1, 1)_White(1, 1, 1) = Black(0, 0, 0)
White(1, 1, 1)_Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
Darker Gray(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)_Lighter Gray(0.5, 0.5, 0.5) = (-0.1, -0.1, -0.1) → Black(0, 0, 0)
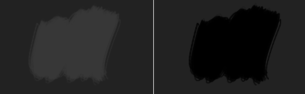
Left: Normal. Right: Subtract.¶
Light Blue(0.1608, 0.6274, 0.8274) - Orange(1, 0.5961, 0.0706) = (-0.8392, 0.0313, 0.7568) → Blue(0, 0.0313, 0.7568)
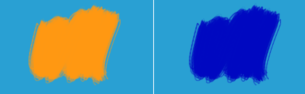
Left: Normal. Right: Subtract.¶
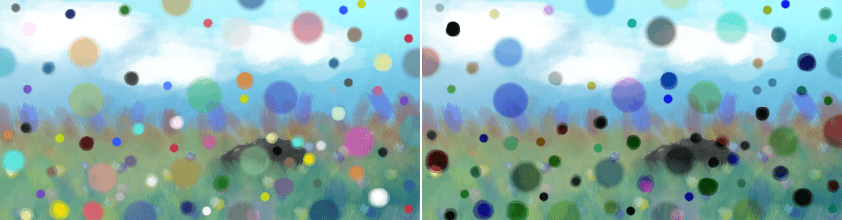
Left: Normal. Right: Subtract.¶