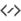Edge Detection¶
Edge detection filters focus on finding sharp contrast or border between colors in an image to create edges or lines.
Since 4.0 there are only two edge detection filters.
Edge Detection¶
Added in version 4.0.
A general edge detection filter that encapsulates all other filters. Edge detection filters that were separate before 4.0 have been folded into this one. It is also available for filter layers and filter brushes.
From left to right: Original, with Prewitt edge detection applied, with Prewitt edge detection applied and result applied to alpha channel, and finally the original with an edge detection filter layer with the same settings as 3, and the filter layer blending mode set to multiply.¶
- Formula
The convolution kernel formula for the edge detection. The difference between these is subtle, but still worth experimenting with.
- Simple
A Kernel that is not square unlike the other two, and while this makes it fast, it doesn’t take diagonal pixels into account.
- Prewitt
A square kernel that includes the diagonal pixels just as strongly as the orthogonal pixels. Gives a very strong effect.
- Sobel
A square kernel that includes the diagonal pixels slightly less strong than the orthogonal pixels. Gives a more subtle effect than Prewitt.
- Output
The output.
- All sides
Convolves the edge detection into all directions and combines the result with the Pythagorean theorem. This will be good for most uses.
- Top Edge
This only detects changes going from top to bottom and thus only has top lines.
- Bottom Edge
This only detects changes going from bottom to top and thus only has bottom lines.
- Right Edge
This only detects changes going from right to left and thus only has right lines.
- Left Edge
This only detects changes going from left to right and thus only has left lines.
- Direction in Radians
This convolves into all directions and then tries to output the direction of the line in radians.
- Horizontal/Vertical radius
The radius of the edge detection. Default is 1 and going higher will increase the thickness of the lines.
- Apply result to Alpha Channel.
The edge detection will be used on a grayscale copy of the image, and the output will be onto the alpha channel of the image, meaning it will output lines only.
Gaussian High Pass¶
A High Pass filter is a type of edge detection filter. It is usually used to enhance contrasts, much like a sharpen filter, but within a texture editing workflow it is also used to remove local gradients.
- Radius
The radius within the Gaussian High Pass filter is similar to the radius in the Edge Detection filter.
To use this as a sharpen filter, create a filter layer with this filter, and then set the blending mode to modes like ‘soft light’, ‘overlay’, ‘hard light’, ‘linear light’. Different blending modes give different results.
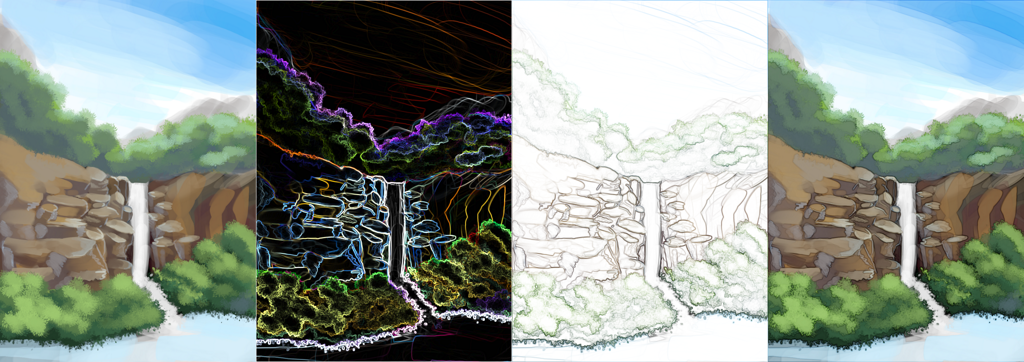
Top left: Original, top right: Gaussian Highpass Result with radius 3, bottom left: Gaussian High Pass Result with radius 3 blended over the original with to Linear Light, bottom right: Gaussian High Pass result with radius 3 blended over the original with Soft Light.¶
To remove local gradients from a texture, create a clone layer, and apply this filter as a filter mask. Then, put a filter layer with gaussian blur set to the full amount in between the clone layer and the original. Finally, set the clone layer to luminosity or multiply (in this case an extra filter mask needs to be added to reduce the levels so that the multiplication result will not be as strong).
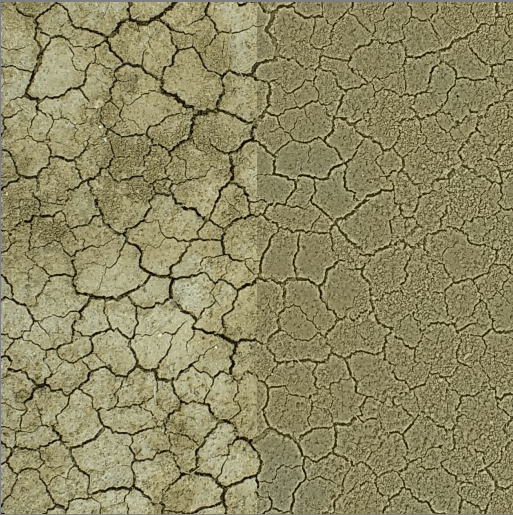

Left: Original, top right: Gaussian High Pass Result blended with luminosity to remove the local gradients but keep the sharp details. In this specific example the lack of local gradients removes some character, but the gaussian high pass result could also be used to create a heightmap.¶
Height to Normal Map¶
Added in version 4.0.
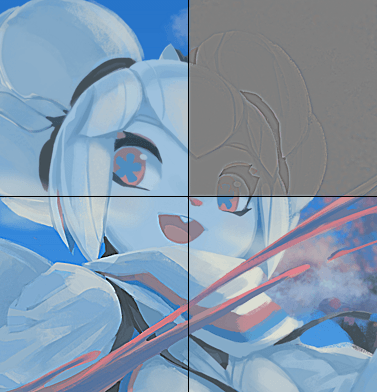
A filter that converts Height maps to Normal maps through the power of edge detection. It is also available for the filter layer or filter brush.
- Formula
The convolution kernel formula for the edge detection. The difference between these is subtle, but still worth experimenting with.
- Simple
A Kernel that is not square unlike the other two, and while this makes it fast, it doesn’t take diagonal pixels into account.
- Prewitt
A square kernel that includes the diagonal pixels just as strongly as the orthogonal pixels. Gives a very strong effect.
- Sobel
A square kernel that includes the diagonal pixels slightly less strong than the orthogonal pixels. Gives a more subtle effect than Prewitt.
- Channel
Which channel of the layer should be interpreted as the grayscale heightmap.
- Horizontal/Vertical radius
The radius of the edge detection. Default is 1 and going higher will increase the strength of the normal map. Adjust this if the effect of the resulting normal map is too weak.
- XYZ
An XYZ swizzle, that allows you to map Red, Green and Blue to different 3d normal vector coordinates. This is necessary mostly for the difference between MikkT-space normal maps (+X, +Y, +Z) and the OpenGL standard normal map (+X, -Y, +Z).